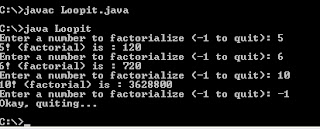
import java.io.*;
class Loopit {
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader
(new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int count, max, num;
num = 0; // Assign initial value of count
while (num != -1) {
System.out.print ("Enter a number to factorialize (-1 to quit): ");
System.out.flush();
num = Integer.parseInt (stdin.readLine());
max = 1; // Assign to 1, so factorial isn't zero every time
if (num == -1) {
System.out.println("Okay, quiting...");
}
else { // Since they're not quitting we better factorialize
for (count = 1; count<=num; count++) {
max = count * max;
}
System.out.println (num+"! (factorial) is : "+ max);
}
}
} // method main
}
class Loopit {
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader
(new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int count, max, num;
num = 0; // Assign initial value of count
while (num != -1) {
System.out.print ("Enter a number to factorialize (-1 to quit): ");
System.out.flush();
num = Integer.parseInt (stdin.readLine());
max = 1; // Assign to 1, so factorial isn't zero every time
if (num == -1) {
System.out.println("Okay, quiting...");
}
else { // Since they're not quitting we better factorialize
for (count = 1; count<=num; count++) {
max = count * max;
}
System.out.println (num+"! (factorial) is : "+ max);
}
}
} // method main
}
No comments:
Post a Comment